|
|
GUI - Precession Settings > Dr. Probe / Documentation / GUI / Calculation / Setup |

|
Precession diffraction is a calculation type where a diffraction pattern is integrated while changing the incident beam tilt.
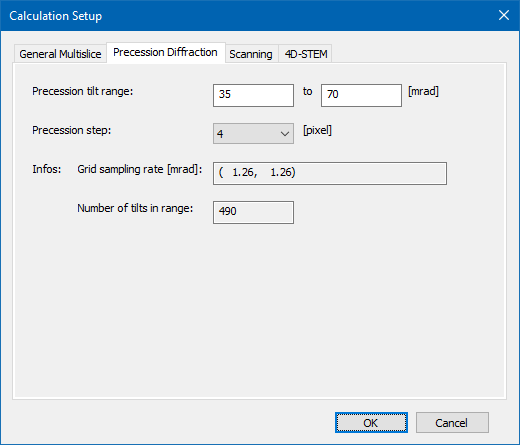
The two parameters define the amount of beam tilt used in a precession tilt simulation where the left value entered refers to the smallest and the right value to the largest tilt magnitude in mrad units.
The program determines which beams of the numerical diffraction plane fall into the specified range and will calculate a diffraction pattern for each respective incident probe tilt and post-specimen de-scan tilt. A calculation with minimum and maximum tilt magnitude set to the same value will still cover a range approximately corresponding to the Fourier space sampling rate of the simulation (displayed below), i.e. to the inverse of the size of the super-cell. The resulting precession tilt diffraction pattern is calculated as the total sum of all tilted patterns with a final normalization to the total incident beam current.
The precession step can be selected from a dropdown list with values between 1 and 10. A step size of 1 will include every numerical Fourier coefficient providing maximum accuracy but also leading to long calculation times. Larger step sizes will exclude beam tilts corresponding to numerical Fourier coefficients in a regular pattern. This can reduce accuracy or convergence of the tilt precession calculation but reduces calculation time. An estimate of the number of precession tilts for the current microscope and sample parameters is given.
Last update: April 25, 2022 contact disclaimer(de)